Copper Oxide nanoparticles (CuO) is the oxide of copper(II) that in its nanocrystalline form finds many applications as a heterogeneous and electro-catalyst, especially for the valorization of CO2.
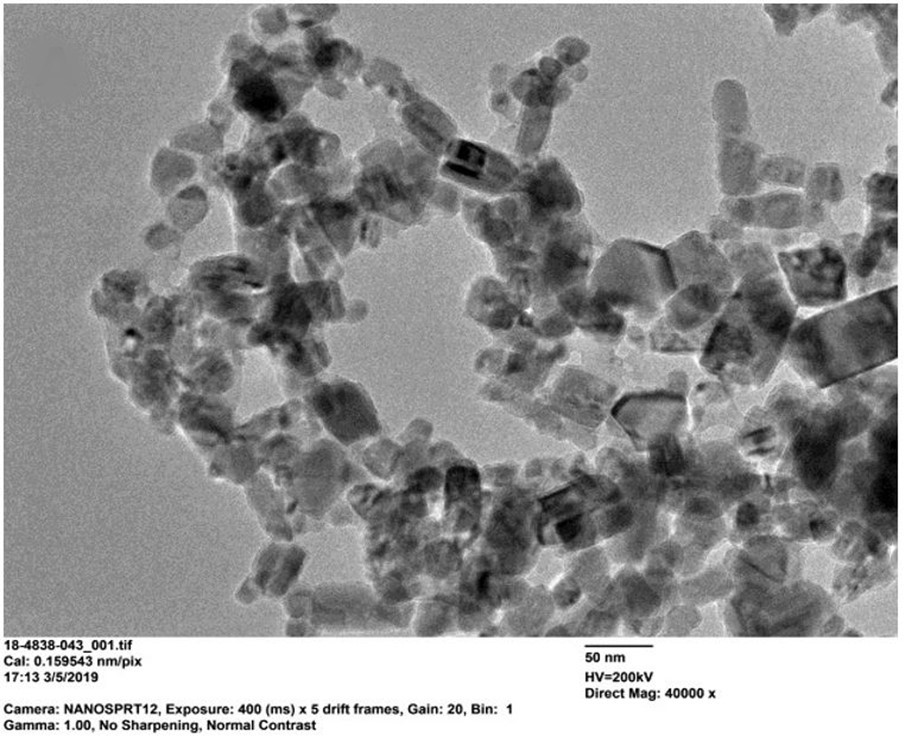

We at Particular Materials synthesize and supply nano CuO and we produce dispersions with excellent stability, monodispersity and fully disaggregated state.
- To buy CuO nanoparticles nanopowders and nanodispersions, and for information on pricing, click and request a free quotation now,
- For a Technical Request and for tailor made nanomaterials, don’t hesitate to ask for free support now, click here.
Technical Information
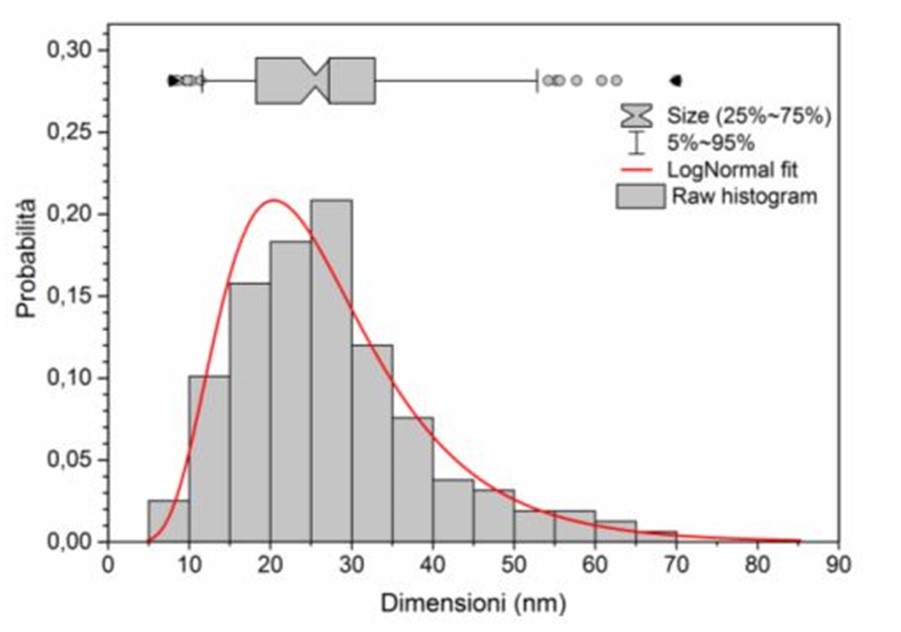
Our Copper oxide (CuO) nanoparticles portfolio consist of particles with diameters ranging around 40 nanometers and find applications in several industries.
CuO nanoparticles are generally insoluble in aqueous (water) solutions and highly stable in solid matrices, making them useful in simple ceramic structures for advanced electronics and in highly flexible components in aerospace and electrochemical applications such as fuel cells in which they exhibit ionic conductivity.
Oxide compounds are not conductive to electricity. However, certain perovskite structured oxides are electronically conductive finding application in the cathode of solid oxide fuel cells and oxygen generation systems.
In order to be able to take advantage of the various properties of Copper Oxide (CuO) nanoparticles, significant care needs to be taken in controlling size, monodispersity and crystalline structure.
We at Particular Materials synthesize nano CuO and we produce dispersions with excellent stability, monodispersity, crystalline purity and fully disaggregated state.
The CuO nanoparticles are available in two sizes:
- 10 nm
- 20 nm
Typical concentration in water are, by weight (w/w%):
- 1%
- 5%
- 10%
- 20%
Copper oxide (CuO) nanoparticles can also be provided as nanopowder.
- For specific requirements please send a Technical Support Request
- For a Technical Request and for tailor made nanomaterials, don’t hesitate to ask for free support now, click here.
Related Applications and Industries
Other key applications of copper oxide nanoparticles are as follows:
- semiconductors, solar energy transformation, and high-tech superconductors
- catalyst for the rate of combustion in rocket propellant
- photoconductors and photothermal systems
- Gas sensors, magnetic storage media, near-infrared tilters
- used as a cathode of solid oxide fuel cells and oxygen generation systems.
A peculiar characteristic of all nanoparticles is the high surface area to volume ratio, that allows a considerably higher binding capacity and excellent dispersibility of NPs in solutions.
Pricing
Selected nanotechnology research articles
Green synthesis, morphological and optical studies of CuO nanoparticles. Journal of Molecular Structure, Volume 1150, Pages 553-557. K. Rayapa Reddy. 2017.
Eco-friendly Mycogenic Synthesis of ZnO and CuO Nanoparticles for In Vitro Antibacterial, Antibiofilm, and Antifungal Applications. Biol Trace Elem Res 199, 2788–2799 (2021). Mohamed, A.A., Abu-Elghait, M., Ahmed, N.E. et al.
ZnO and CuO nanoparticles: a threat to soil organisms, plants, and human health. Environ Geochem Health 42, 147–158 (2020). Rajput, V., Minkina, T., Sushkova, S. et al.
Methods of Synthesis, Properties and Biomedical Applications of CuO Nanoparticles. Pharmaceuticals 2016. Grigore M.E. , Biscu E.R. , Holban A.M. et al.
Nearly Monodisperse Cu2O and CuO Nanospheres: Preparation and Applications for Sensitive Gas Sensors Jiatao ZhangJunfeng LiuQing PengXun WangYadong Li, Chem. Mater.2006184867-871.
Characterisation of copper oxide nanoparticles for antimicrobial applications G Ren, D Hu, EWC Cheng, MA Vargas-Reus, nternational Journal of Antimicrobial Agents Volume 33, Issue 6, June 2009, Pages 587-5