Lithium Iron phosphate LiFePO4 (LFP) is extensively used in the Lithium ion battery field as cathode material. The main advantages of LFP are its flat voltage profile, low material cost, abundant material supply and better environmental compatibility compared to other cathode materials. All these characteristics makes LFP one of the benchmark materials for energy storage applications.
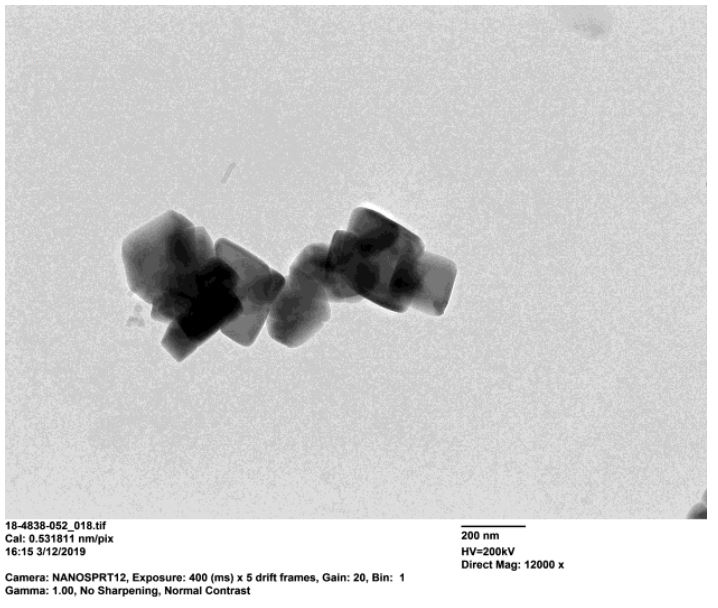

We at Particular Materials synthesize nano LFP and we produce and supply dispersions with excellent stability, monodispersity and fully disaggregated state.
- To buy LFP nanoparticles nanopowders and nanodispersions, and for information on pricing, click and request a free quotation now,
- For a Technical Request and for tailor made nanomaterials, don’t hesitate to ask for free support now, click here.
Technical Information
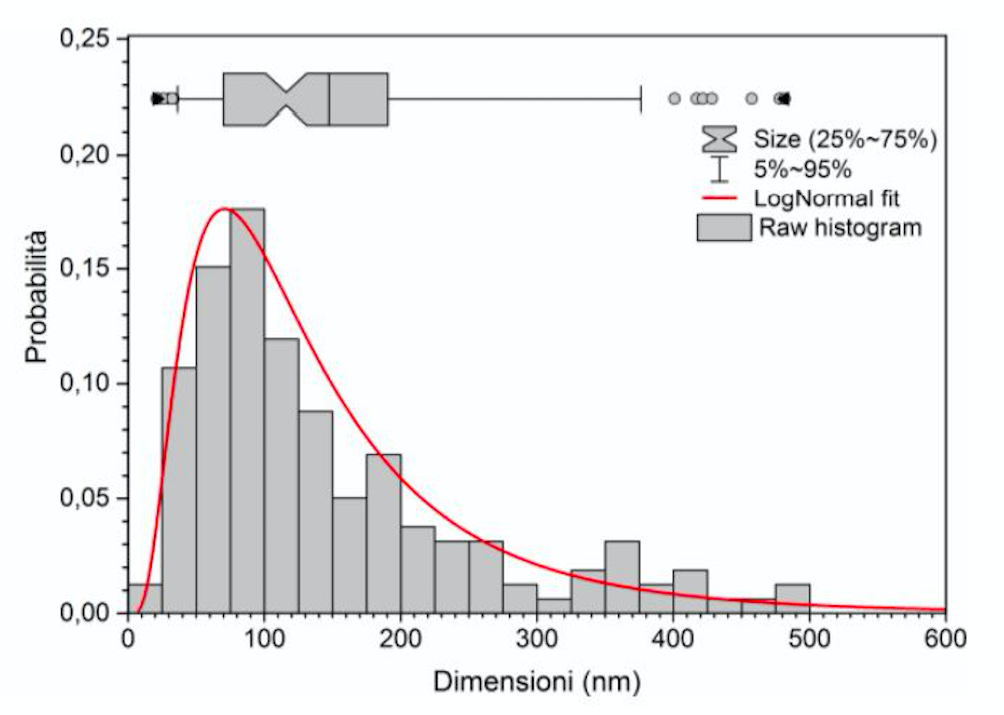
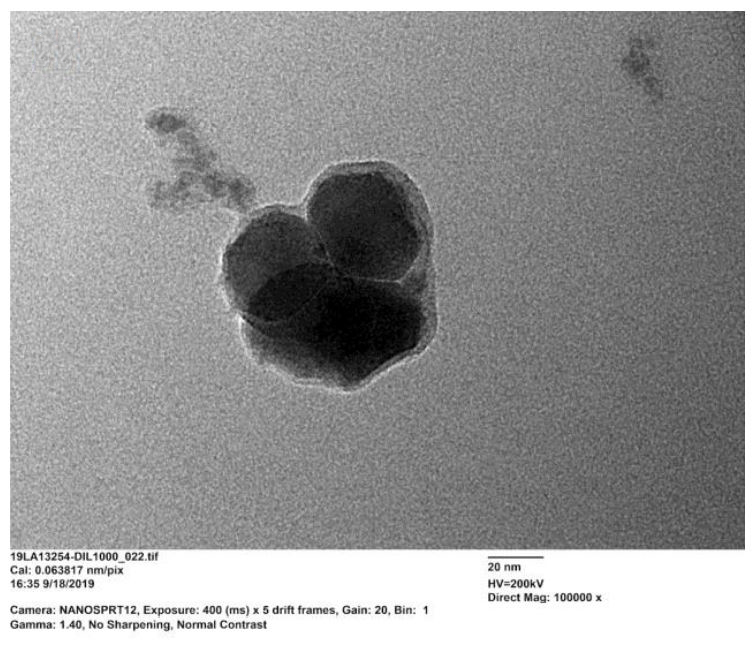
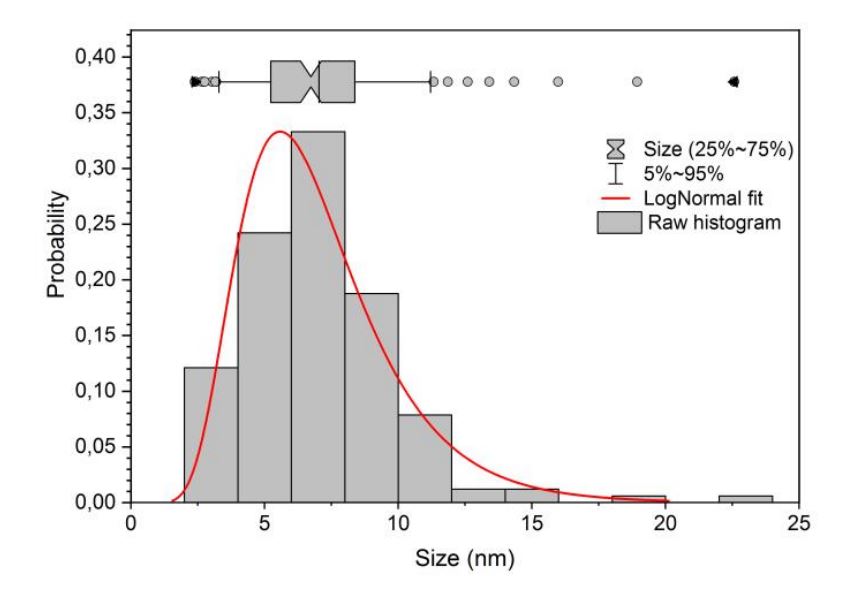
Tipically, our Lithium iron phosphate LiFePO4 (LFP) nanoparticles have a mean diameter of 90 nanometers, whereas carbon-coated LFP nanoparticles have a mean diameter below 10 nanometers.
Since poor electronic and ionic conductivity of the bare LFP nanoparticles could lead to several limitation in their practical use, we developed a peculiar treatment during the synthetic process to cover the single nanoparticle with a conductive carbon coating.
In order to be able to take advantage of the various properties of Lithium iron phosphate (LFP) nanoparticles, significant care needs to be taken in controlling size, monodispersity and crystalline structure.
We at Particular Materials synthesize nano LiFePO4 (LFP) and we produce dispersions with excellent stability, monodispersity, crystalline purity and fully disaggregated state.
The LFP nanoparticles are available in two different formats:
- LFP
- LFP + carbon coating
Typical concentration in water are, by weight (w/w%):
- 1%
- 5%
- 20%
- 40%
- 60%
LFP can also be provided as nanopowder.
- For specific requirements please send a Technical Support Request
- For a Technical Request and for tailor made nanomaterials, don’t hesitate to ask for free support now, click here.
Related Applications and Industries
Lithium based batteries are dominating the scenes in large-scale applications such as electric vehicles and backup power systems but also in consumer electronics like smartphone and notebooks.
Compared to others Lithium based technologies, LFP contain neither nickel nor cobalt, both of which are supply-constrained and expensive. The use of phosphates avoids cobalt’s cost and environmental concerns, particularly concerns about cobalt entering the environment through improper disposal.
Furthermore, LFP chemistry offers a longer cycle life than other lithium-ion approaches. Carbon coating was demonstrated to be the most efficient way to improve the conductivity and rate performance of LFP.
Some electronic cigarettes use these types of batteries. Other applications include flashlights, radio-controlled models, portable motor-driven equipment, amateur radio equipment, industrial sensor systems and emergency lighting.
Pricing
Selected nanotechnology research articles
Li ion battery materials with core–shell nanostructures. Liwei Su, Yu Jing and Zhen Zhou, Nanoscale, 2011, 3, 3967.
Challenges in the development of advanced Li-ion batteries: a review. Vinodkumar Etacheri, Rotem Marom, Ran Elazari, Gregory Salitra and Doron Aurbach, Energy Environ. Sci., 2011, 4, 3243.