Titanium oxide nanoparticles (TiO2, anatase) are the most explored photocatalytic nanoparticles, and they have extensive application within catalysis, self cleaning, UV-shilding, optical filters, organic photovoltaic (OPV), organic and printed electronics, and many others.
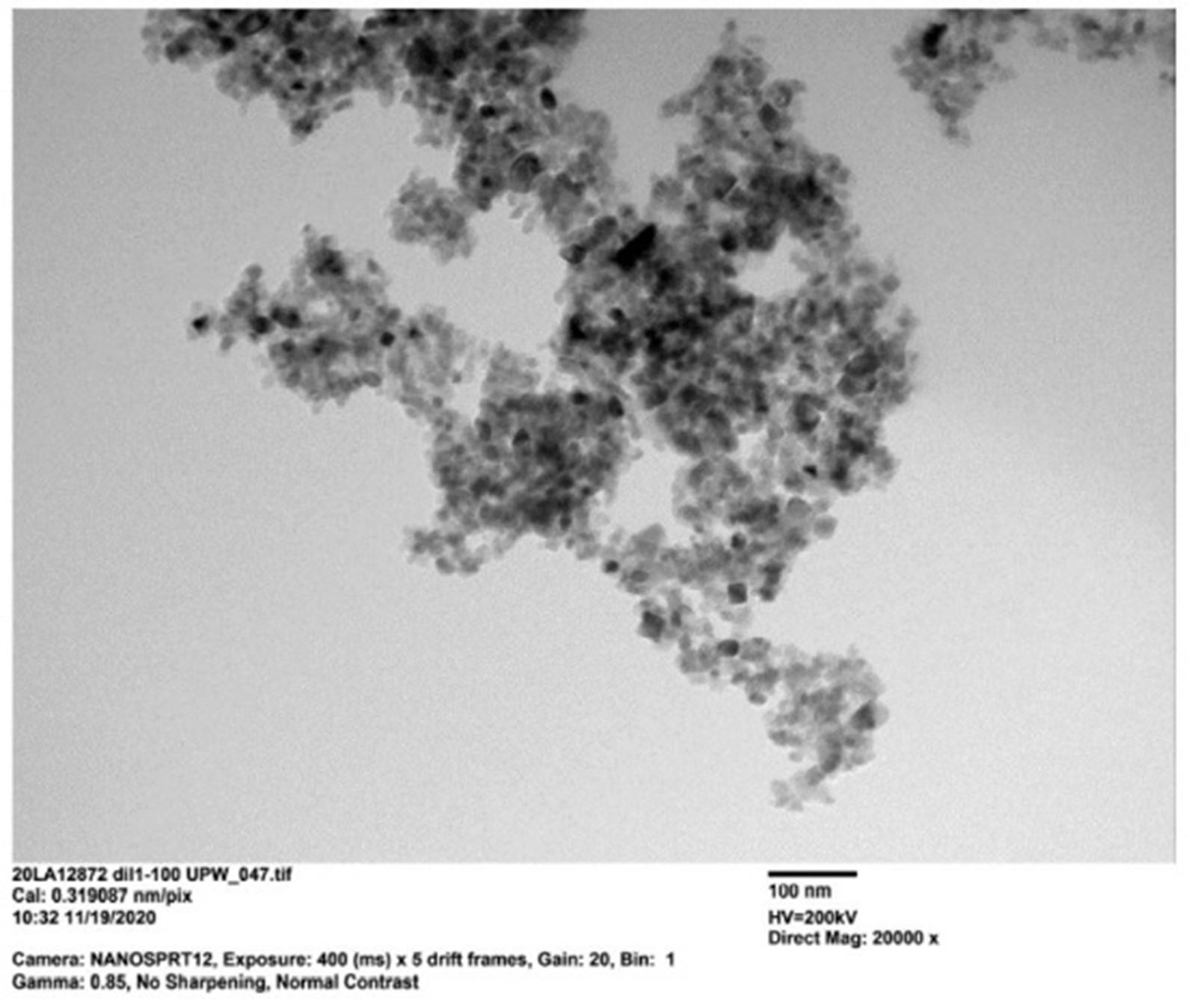
We at Particular Materials synthesize and supply TiO2 nanoparticles and we produce nanodispersions in water and in organic solvents, with excellent stability, monodispersity and fully disaggregated state.
- To buy TiO2 nanoparticles nanopowders and nanodispersions, and for information on pricing, click and request a free quotation now.
- For a Technical Request and for tailor made nanomaterials, don’t hesitate to ask for free support now, click here.
Technical Information
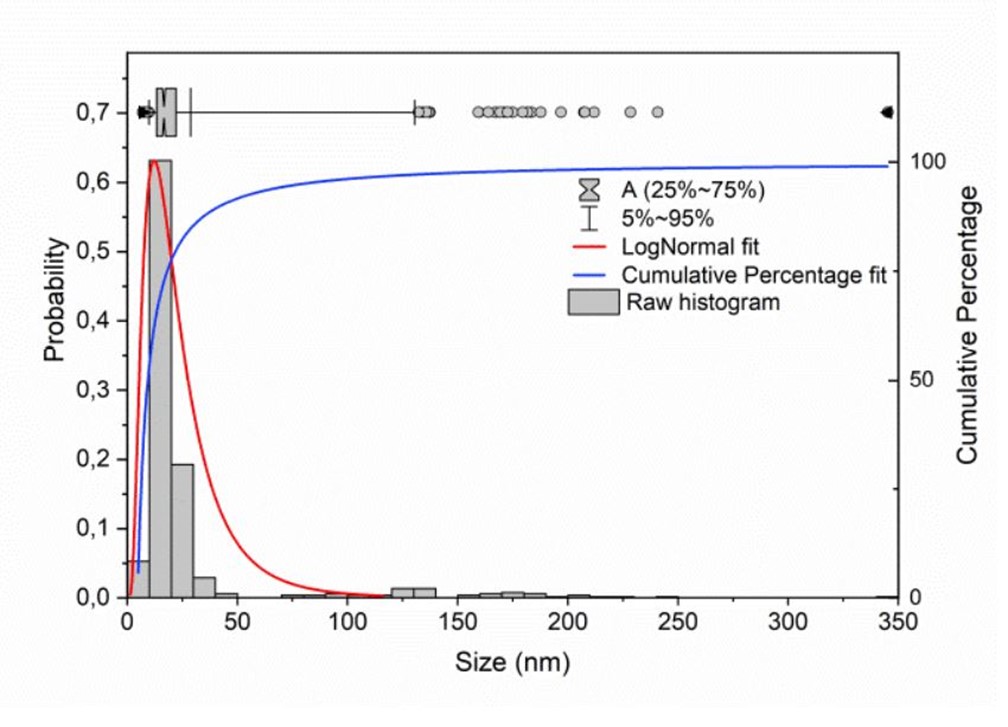
Our Titanium oxide (TiO2 , anatase) nanoparticles portfolio consist of particles with diameters ranging from 5 to 15 nanometers and find applications in several industries.
TiO2 nanoparticles with sizes below 20 nm display UV absorption behavior without light scattering and they are extensively employed as inorganic UV filter. The advantage of using monodisperse nanoparticles is better understood when we think that scattering phenomena are largely size dependent: a broad distribution of nanoparticles will increase the probability of light scattering phenomena, limiting the transparency of a coating.
In order to be able to take advantage of the various properties of Titanium Oxide (TiO2) nanoparticles, significant care needs to be taken in controlling size, monodispersity and crystalline structure.
We at Particular Materials synthesize and supply TiO2 nanoparticles and we produce nanodispersions in water and in organic solvents, with excellent stability, monodispersity, crystalline purity and fully disaggregated state.
The TiO2 nanoparticles are available in two different sizes:
- 4.8 ± 0.9 nm
- 15.2 ± 3.5 nm
Typical concentration in water are, by weight (w/w%):
- 1%
- 5%
- 10%
- 20%
TiO2 can also be provided as nanopowder.
- For specific requirements please send a Technical Support Request
- For a Technical Request and for tailor made nanomaterials, don’t hesitate to ask for free support now, click here.
Related Applications and Industries
One of the primary uses of TiO2 nanoparticles is for its inherent UV-resistance, making it a crucial ingredient in various coatings and materials as UV screen.
Another key usage of titanium oxide nanoparticles is in the production of self-cleaning materials, such as self-cleaning glasses and ceramics.
The optical properties of titanium oxide nanoparticles makes it of value in the production of certain printing inks. Dispersibility and stability of the colloidal dispersion is of paramount importance.
Many cosmetics utilize titanium oxide nanoparticles for its unique antibacterial and optical properties. This includes moisturizers, beauty creams, whitening creams, vanishing creams, sunscreens, powdered make-up, skin rinses, and many other products.
Various organic substances degrade when exposed to titanium oxide nanoparticles, making it useful in certain decontamination efforts and in the treatment of sewage and organic chemical waste products. Due to its photo-catalytic properties, titanium oxide nanoparticles can serve as a key ingredient in various antibacterial and antiseptic compounds.
A peculiar characteristic of all nanoparticles is the high surface area to volume ratio, that allows a considerably higher binding capacity and excellent dispersibility of NPs in solutions.
Pricing
Selected nanotechnology research articles
Exploring potential Environmental applications of TiO2 Nanoparticles. Adawiya J. Haider, Riyad Hassan AL– Anbari, Ghadah Rasim Kadhim, Chafic Touma Salame. Energy Procedia, Volume 119, Pages 332-345. 2017
Application of titanium dioxide (TiO2) nanoparticles in cancer therapies. Selin Cesmeli, Cigir Biray Avci. 2018, Pages 762-766
TiO2 nanoparticles immobilized organo-reduced graphene oxide hybrid nanoreactor for catalytic applications. Subodh, Karan Chaudhary, Kunal Prakash, Dhanraj T. Masram. Applied Surface Science, Volume 509, 2020, 144902, ISSN 0169-4332
Size controlled synthesis of TiO2 nanoparticles by modified solvothermal method towards effective photo catalytic and photovoltaic applications. V. M. Ramakrishnan, et al. Materials Research Bulletin, Volume 97, 2018, Pages 351-360, ISSN 0025-5408
Reversible Photodoping of TiO2 Nanoparticles for Photochromic Applications. Urmas Joost, et al.
TiO2 nanoparticles as an effective UV-B radiation skin-protective compound in sunscreens. A P Popov et al 2005 J. Phys. D: Appl. Phys. 38 2564 , 2005
Titanium dioxide photocatalysis. A. Fujishima,T. N. Rao, D. A. Tryk Journal of Photochemistry and Photobiology C: Photochemistry Reviews Volume 1, Issue 1, 29 June 2000, Pages 1-21.
The surface science of titanium dioxide. U. Diebold Surface Science Reports
Volume 48, Issues 5–8, January 2003, Pages 53-229.