Iron Oxide nanoparticles in their magnetite crystal form (Fe3O4) are the most explored magnetic nanoparticles, due to their extensive application within catalysis, biomedicine, photonic crystals, microfluidics, data storage, environmental remediation and optical filters.
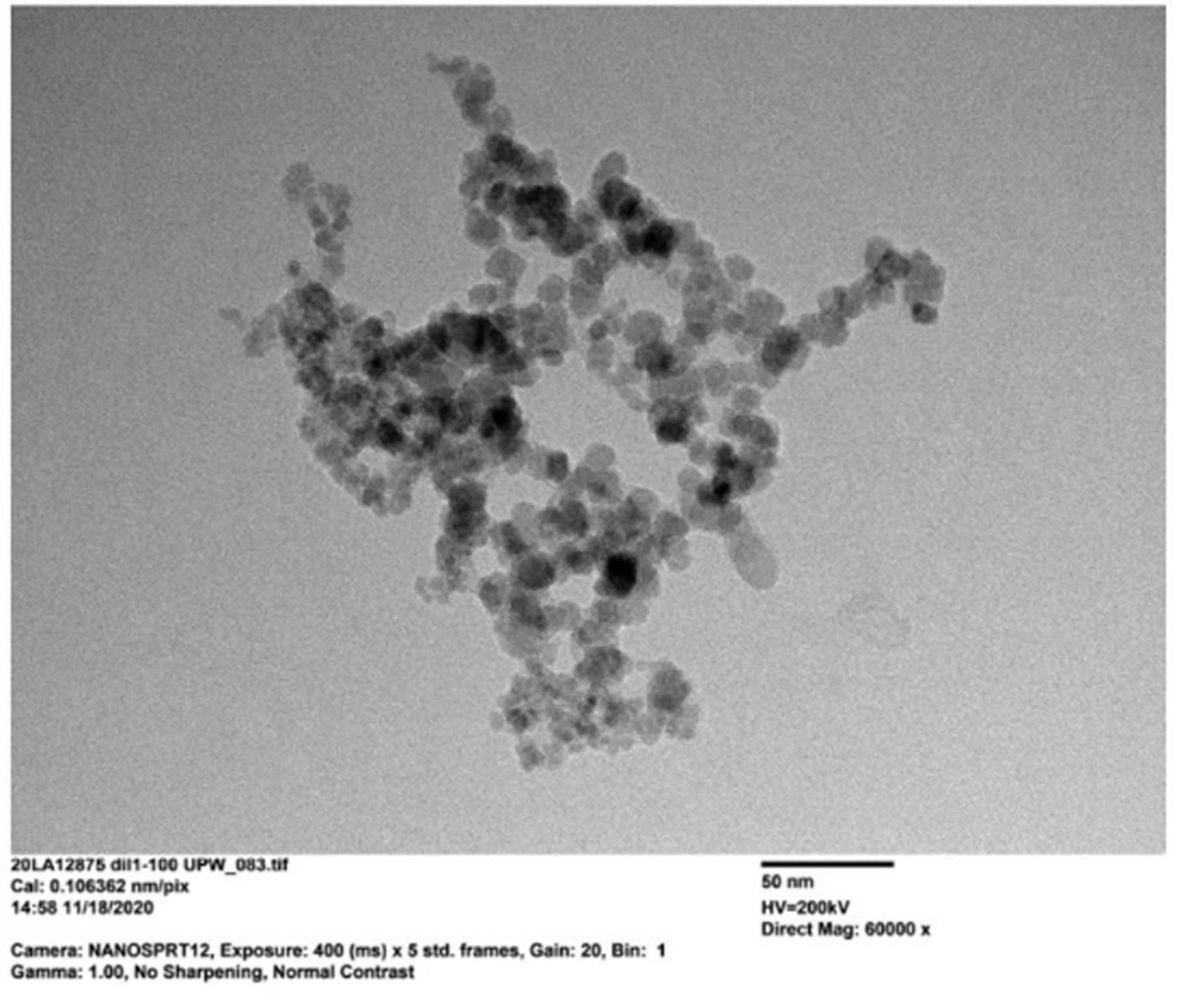
We at Particular Materials synthesize and supply nano magnetic Fe3O4 and we produce dispersions with excellent stability, monodispersity and fully disaggregated state.
- To buy Fe3O4 nanoparticles nanopowders and nanodispersions, and for information on pricing, click and request a free quotation now,
- For a Technical Request and for tailor made nanomaterials, don’t hesitate to ask for free support now, click here.
Technical Information
Our Iron oxide Fe3O4 nanoparticles portfolio consist of magnetite (Fe3O4) particles with diameters ranging from 4 to 70 nanometer and find applications in several industries.
Magnetic NPs, with sizes between 2 and 20 nm display superparamagnetism, i.e. their magnetization is zero, in the absence of an external magnetic field and they can be magnetized by an external magnetic source. This property provides additional stability for magnetic nanoparticles in solutions.
In order to be able to take advantage of the various properties of iron oxide (Fe3O4) nanoparticles, significant care needs to be taken in controlling size, monodispersity and crystalline structure.
For biomedical applications of Fe3O4 nanoparticles it is important to be able to tailor-made the surface properties of the nanoparticles: the difference in surface functional groups influences the behaviour of drug laoding and other parameters, for example.
We at Particular Materials synthesize nano magnetic Fe3O4 and we produce and supply Fe3O4 nano dispersions with excellent stability, monodispersity, crystalline purity and fully disaggregated state.
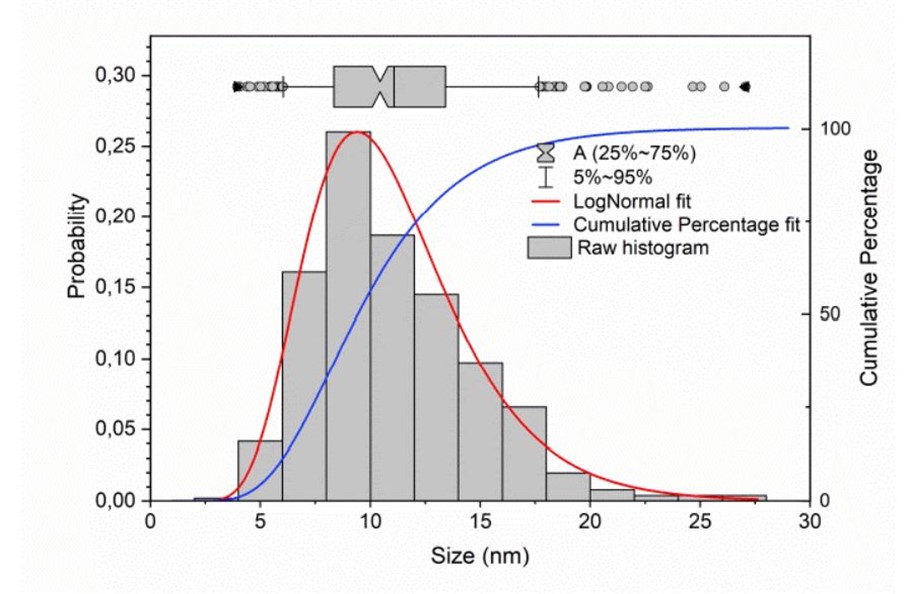
The Fe3O4 nanoparticles are available in four different size:
- 3.6 ± 1.2 nm
- 5.4 ± 1.2 nm
- 7.8 ± 2.9 nm
- 14 ± 6 nm
Typical concentration in water are, by weight (w/w%):
- 1%
- 5%
- 20%
Iron Oxide nanoparticles surface can be modified, and can be carbon coated, coated with organic acids, polymers, amines or any stabilizer of interest. Fe3O4 can also be provided as nanopowder.
- For specific requirements please send a Technical Support Request
- For a Technical Request and for tailor made nanomaterials, don’t hesitate to ask for free support now, click here.
Related Applications and Industries
Fe3O4 nanoparticles have attracted considerable interest due to their superparamagnetic properties and their potential biomedical applications arising from its biocompatibility and non-toxicity.
Among other industries, Iron oxide Fe3O4 nanoparticles are used as magnetic data storage, biosensors, drug-delivery, ferrofluids, magnetic coatings, EM-waves absorbing coatings, wastewater purification.
During magnetic separation, for exaple, the application of a magnetic field enable to selectively collect a magnetic responsive materials such as magnetic iron oxide (Fe3O4) nanoparticles.
This technology is applied to water treatment such as removal of heavy metal ions, pesticide, toxic water soluble molecules, and oily water treatment.
In addition to the applications already mentioned, iron oxide nanoparticles play crucial rules in dozens of other magnetic devices and applications, such as medical imaging, cell separation, and refrigeration.
A peculiar characteristic of all nanoparticles is the high surface area to volume ratio, that allows a considerably higher binding capacity and excellent dispersibility of NPs in solutions.
Pricing
Selected nanotechnology research articles
Surface Study of Fe3O4 Nanoparticles Functionalized With Biocompatible Adsorbed Molecules. Beata Lesiak, N. Rangam, et al.
Green biosynthesis of superparamagnetic magnetite Fe3O4 nanoparticles and biomedical applications in targeted anticancer drug delivery system: A review. Yen Pin Yew, Kamyar Shameli, Mikio Miyake, et al. Arabian Journal of Chemistry, Volume 13, Issue 1, Pages 2287-2308, 2020.
Application of iron oxide (Fe3O4) nanoparticles during the two-stage anaerobic digestion with waste sludge: Impact on the biogas production and the substrate metabolism. Renewable Energy, Volume 146, Pages 2724-2735. Zengshuai Zhang, Liang Guo, Yi Wang, Yangguo Zhao, Zonglian She, Mengchun Gao, Yiding Guo. 2020
Influence of Fe3O4 nanoparticles on the optical, magnetic and electrical properties of PMMA/PEO composites: Combined FT-IR/DFT for electrochemical applications. Journal of Organometallic Chemistry, Volume 92. M.M. Abutalib, A. Rajeh. 2020
Efficacy and safety of intratumoral thermotherapy using magnetic iron-oxide nanoparticles combined with external beam radiotherapy on patients with recurrent glioblastoma multiforme. Maier-Hauff, K., Ulrich, F., Nestler, D. et al. J Neurooncol (2011) 103: 317.
Synthesis, Surface Modification and Characterisation of Biocompatible Magnetic Iron Oxide Nanoparticles for Biomedical Applications. Mahdavi, M.; Ahmad, M.B.; Haron, M.J.; Namvar, F.; Nadi, B.; Rahman, M.Z.A.; Amin, J. Molecules 2013, 18, 7533-7548.
Superparamagnetic Iron Oxide Nanoparticle Probes for Molecular Imaging. Thorek, D.L.J., Chen, A.K., Czupryna, J. et al. Ann Biomed Eng (2006) 34: 23.